Pathophysiology Of Diabetes Vascular Complications
Advances And Pathophysiology Of Vascular Complications Of
Diabetes dramatically increases the risk of various cardiovascular problems, including coronary artery disease with chest pain (angina), heart attack, stroke and narrowing of arteries (atherosclerosis). Diabetes 18, macrovascular complications of diabetes in the peripheral vessels atheroma will result in peripheral vascular disease. diabetes complication and pathophysiology of the. Diabetes is a group of chronic diseases characterized by hyperglycemia. modern medical care uses a vast array of lifestyle and pharmaceutical interventions aimed at preventing and controlling hyperglycemia. in addition to ensuring the adequate delivery of glucose to the tissues of the body, treatment of diabetes attempts to decrease the likelihood that the tissues of the body are harmed by. Patients with diabetes mellitus have other conditions that contribute to foot wounds and exacerbate the complications of vascular insufficiency, such as neuropathy and altered foot mechanics. the presence of these additional complications may make determination of the pathogenesis of pedal ulcers more difficult to ascertain.
in blood sugar homeostasis as well as the pathophysiology of diabetes beta-cells are arranged into distinct pxd101 distributor Macroand microvascular diabetic complications are mainly due to prolonged exposure to hyperglycemia clustering with other risk factors such as arterial hypertension, dyslipidemia as well as genetic susceptibility. 3 interestingly, nephropathy, retinopathy, and diabetic vascular disease are in line with the notion that endothelial, mesangial, and retinal cells are all equipped to handle high sugar levels when compared with other cell types. 4 the detrimental effects of glucose already occur.
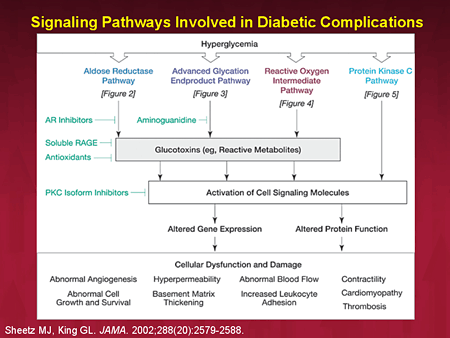
Microvascular complications of diabetes. diabetic retinopathy. diabetic retinopathy may be the most common microvascular complication of diabetes. it is responsible for ∼ 10,000 new diabetic nephropathy. diabetic neuropathy. macrovascular complications of diabetes. practice recommendations. Advances and pathophysiology of vascular complications of diabetes john t gwynne donald e mcmillan diabetes care feb 1991, 14 (2) 148; doi: 10. 2337/diacare. 14. 2. 148. Pieces of the puzzle. the general features of hyperglycemia-induced tissue damage are shown schematically in fig. 1. the dcct (diabetes control and complications trial) and the ukpds (u. k. prospective diabetes study) established that pathophysiology of diabetes vascular complications hyperglycemia, shown on the far left of the figure, is the initiating cause of the diabetic tissue damage that we see clinically, shown on the far right (1,2).
In brief the pathophysiology of the link between diabetes and cardiovascular disease (cvd) is complex and multifactorial. understanding these profound mechanisms of disease can help clinicians identify and treat cvd in patients with diabetes, as well as help patients prevent these potentially devastating complications. this article reviews the biological basis pathophysiology of diabetes vascular complications of the link between diabetes and.
Diabetes And Vascular Disease Pathophysiology Clinical
Diabetes and vascular disease. diabetics have a high incidence of stroke. diabetes is a disease in which the body does not produce or properly use insulin. insulin is a hormone that is needed to convert sugar, starches, and other food into energy needed for daily life. there are several types of diabetes:. Duration of diabetes is an important factor in the pathogenesis of complications, but other risk factors—for example, hypertension, cigarette smoking, and hypercholesterolaemia—interact with diabetes to affect the clinical course of microangiopathy and macroangiopathy. Introduction. the vascular complications pathophysiology of diabetes vascular complications of diabetes are the most serious manifestations of the disease. atherosclerosis is the main reason for impaired life expectancy in patients with diabetes whereas diabetic nephropathy and retinopathy are the largest contributors to end-stage renal disease and blindness, respectively.
Diabetes And Vascular Disease Vascular Cures
Diabetes 18 Macrovascular Complications Of Diabetes Youtube
Six diabetes-related vascular complications and how to avoid them november 8, 2016 but some may not understand that many of the most common complications of diabetes stem from one primary issue: the havoc that high blood sugar, also called hyperglycemia, causes for the body's blood vessels. The chronic complications of diabetes are traditionally classified as macroor microvascular depending on the underlying pathophysiology. the microvascular triad of retinopathy, nephropathy and neuropathy is unique to diabetes. 1 most patients with diabetes will have one or more of these as overt or subclinical manifestations during the course of their disease.
Pathophysiology. the underlying driver of microvascular disease is tissue exposure to chronic hyperglycaemia. landmark clinical trials such as the uk prospective diabetes study (ukpds) and diabetes control of complications trial (dcct) have established a clear relationship between microvascular disease and glucose control. 2,3 microvascular disease tends to occur predominantly in tissues where. Vascular complications of diabetes. in the mi and pad cohorts, there was a significant 16% reduction in death from cardiovascularcauses, mi, or stroke. the benefit for patients with diabetes mellitus and a history of mi was significantly greater than in patients without diabetes mellitus,. Diabetes is linked to several vascular diseases: retinopathy, which is an abnormal growth of blood vessels in your retina nephropathy, a disease that damages the tiny filtering units of the kidney neuropathy, a condition causing a loss of sensation in the feet and toes.
Adults with diabetes have an annual mortality of about 5. 4% (double the rate for non-diabetic adults), and their life expectancy is decreased on average by 5-10 years. although the increased death rate is mainly due to cardiovascular disease, deaths from non-cardiovascular causes are also increased. a diagnosis of diabetes immediately increases the risk of developing various clinical. Pathophysiology behind symptoms and complications of diabetes polydipsia or increased thirst is due to high blood glucose that raises the osmolarity of blood and makes it more concentrated.
Macrovascular complications include cardiovascular diseases such as heart attacks, strokes and insufficiency in blood flow to legs. there is evidence from large randomized-controlled trials that good metabolic control in both type 1 and 2 diabetes can delay the onset and progression of these complications. Diabetes macrovascular complications are diseases of the blood vessels caused in diabetes patients, influenced by factors like high cholesterol, insulin resistance, smoking, high blood sugar, high blood pressure and blood clotting disorders. there are three main macro vascular complications of diabetes that happen due to an increased risk of atherosclerosis.
Main text introduction. the vascular complications of diabetes are among the most serious manifestations of the disease. atherosclerosis is the main reason for impaired life expectancy in patients with diabetes, whereas diabetic nephropathy and retinopathy are the largest contributors to end-stage renal disease and blindness, respectively. More pathophysiology of diabetes vascular complications images.
Diabetes complication and pathophysiology of the complication chronic complications of diabetes: 14:09. matthew mcpheeters 30,139 views. 14:09. diabetes type ii pathophysiology duration:. Eventually, diabetes pathophysiology of diabetes vascular complications complications may be disabling or even life-threatening. possible complications include: cardiovascular disease. diabetes dramatically increases the risk of various cardiovascular problems, including coronary artery disease with chest pain (angina), heart attack, stroke and narrowing of arteries (atherosclerosis).
Advances in understanding the vascular pathology of diabetes have made it clear that the pathogenesis of diabetic vascular complications is determined by a balance between molecular mechanisms of injury and endogenous protective factors (fig. 1). both aspects of disease mechanisms provide targets for prevention even during suboptimal metabolic control. doses of mercury have a harmful effect on vascular function mercedes salaices, one of the other authors of the study, emphasises that the impact of mercury “could be compared to the impact produced by other more traditional cardiovascular risk factors such as hypertension, diabetes or hypercholesterolaemia” the researchers analysed whether chronic exposure In conjunction with national diabetes awareness month in november, here is how pathophysiology of diabetes vascular complications six vascular complications are aggravated by diabetes: diabetic eye disease. diabetes' effect on the vascular system is what causes diabetic eye disease. the tiny blood vessels in the retina become swollen, which blocks the oxygen supply to the retina. Mitochondrial ros also increase intracellular levels of the glucose metabolite methylglyoxal and ages synthesis. 12,29,30 in experimental diabetes, methylglyoxal is a key player in the pathophysiology of diabetic complications through oxidative stress, ages accumulation, and endothelial dysfunction. 29,31 generation of ages leads to cellular.
Comments
Post a Comment