Diabetes Insipidus Vs Cerebral Salt Wasting
Cerebral Saltwasting Syndrome Wikipedia
Cerebralsalt-wasting syndrome diabetes insipidus vs cerebral salt wasting and central diabetes insipidus. a retrospective study by wu et al found that distinctive features of combined central diabetes insipidus and cerebral salt-wasting syndrome following traumatic brain injury include massive polyuria (the most typical presentation) that responds to vasopressin plus cortisone acetate but not to vasopressin alone, low central venous.
Cerebralsalt-wasting syndrome (csws) is a rare endocrine condition featuring a low blood sodium concentration and dehydration in response to injury (trauma) or the presence of tumors in or surrounding the brain. in this condition, the kidney is functioning normally but excreting excessive sodium. the condition was initially described in 1950. its cause and management remain controversial. Central diabetes insipidus and cerebral salt wasting syndrome may occur at various times during acute brain insult. lee et al. reviewed the literature on 28 pediatric cases of central diabetes insipidus due solely to severe hypoxic ischemia. the intervals between the hypoxic insult and the onset of diabetes insipidus (seen in 23 of 28 cases. Cerebral salt-wasting syndrome, or renal salt wasting, may be more common than siadh and may even occur in the absence of cerebral disease. [ 4 5 7 ] although the exact mechanism that underlies the development of cerebral salt-wasting syndrome is unclear, it is known that the initiating defect in renal sodium transport leads to. It can be associated with the syndrome of inappropriate adh secretion (siadh), cerebral salt wasting (csw), treatment of transient/permanent diabetes insipidus (di), and excessive fluid administration in patients with adipsia. these conditions may occur in isolation or may coexist.
How Are Urine Studies Used To Differentiate Siadh From
Cerebralsalt-wasting syndrome, or renal salt wasting, may be more common than siadh and may even occur in the absence of cerebral disease. [ 4 5 7 ] although the exact mechanism that underlies the development of cerebral salt-wasting syndrome is unclear, it is known that the initiating defect in renal sodium transport leads to. Introduction: combined central diabetes insipidus (di) and cerebral salt wasting syndrome (csw) is a rare clinical finding. however, when this happens, mortality is high due to delayed diagnosis and/or inadequate treatment. Patients with less than 4 days between onset of diabetes insipidus and onset of cerebral salt wasting syndrome were more likely to have a higher mortality rate (7 of 7 died) than those with more than 4 days between onset of the two diseases (3 of 9 died), but the difference was not statistically significant (p = 0. 213). a more detailed timeline.
Cerebralsaltwastingvs lastly, demeclocycline is an option, which actually causes a form of nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. it is unpredictable and does have a lag effect of 3-4 days. it also has an unfortunate effect of causing acute kidney injury,. Diabetesinsipidus. in diabetesinsipidus, or di, the body releases too less anti-diuretic diabetes insipidus vs cerebral salt wasting hormone (adh). it is a disorder of water and salt metabolism marked by extreme thirst and heavy urination. diabetes insipidus di takes place when the body is unable to regulate the fluids. Wu x, zhou x, gao l, et al. diagnosis and management of combined central diabetes insipidus and cerebral salt wasting syndrome after traumatic brain injury. world neurosurg. 2016 apr. 88:483-7.
Natriuresis with polyuria is common after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage (asah). previous studies have shown an increased risk of symptomatic cerebral vasospasm or delayed cerebral ischemia (dci) in patients with hyponatremia and/or the cerebral salt wasting syndrome (csw). however, natriuresis may occur in the absence of hyponatremia or hypovolemia and it is not known whether the increase. Cerebral salt-wasting syndrome (csws) is a rare endocrine condition featuring a low blood sodium concentration and dehydration in response to injury (trauma) or the presence of tumors in or surrounding the brain. in this condition, the kidney is functioning normally but excreting excessive sodium. the condition was initially described in 1950. Central neurogenic diabetes insipidus, syndrome of inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone, and cerebral salt-wasting syndrome are secondary events that affect patients with traumatic brain injury. all 3 syndromes affect both sodium and water balance; however, they have differences in pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment.
How are urine studies used to differentiate siadh from.
Findings in this randomized clinical trial, 36 patients with tuberculous meningitis with cerebral salt wasting were randomized to receive either an 0. 9% solution of intravenous saline and 5 to 12 grams of oral salt supplementation per day or saline, oral salt, and 0. 1 to 0. 4 mg fludrocortisone per day. patients treated with fludrocortisone. Configctrl2. info. metadescription. Lin jj, lin kl, hsia sh, et al. combined central diabetes insipidus and cerebral salt wasting syndrome in children. pediatr neurol. 2009 feb. 40(2):84-7. [medline].
Cerebralsaltwasting Syndrome Practice Essentials
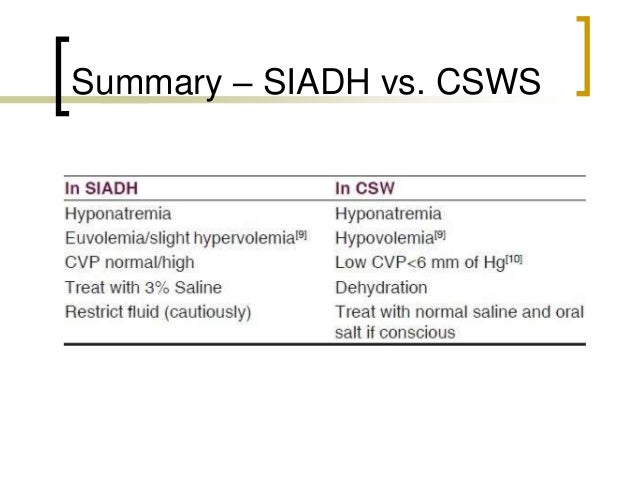
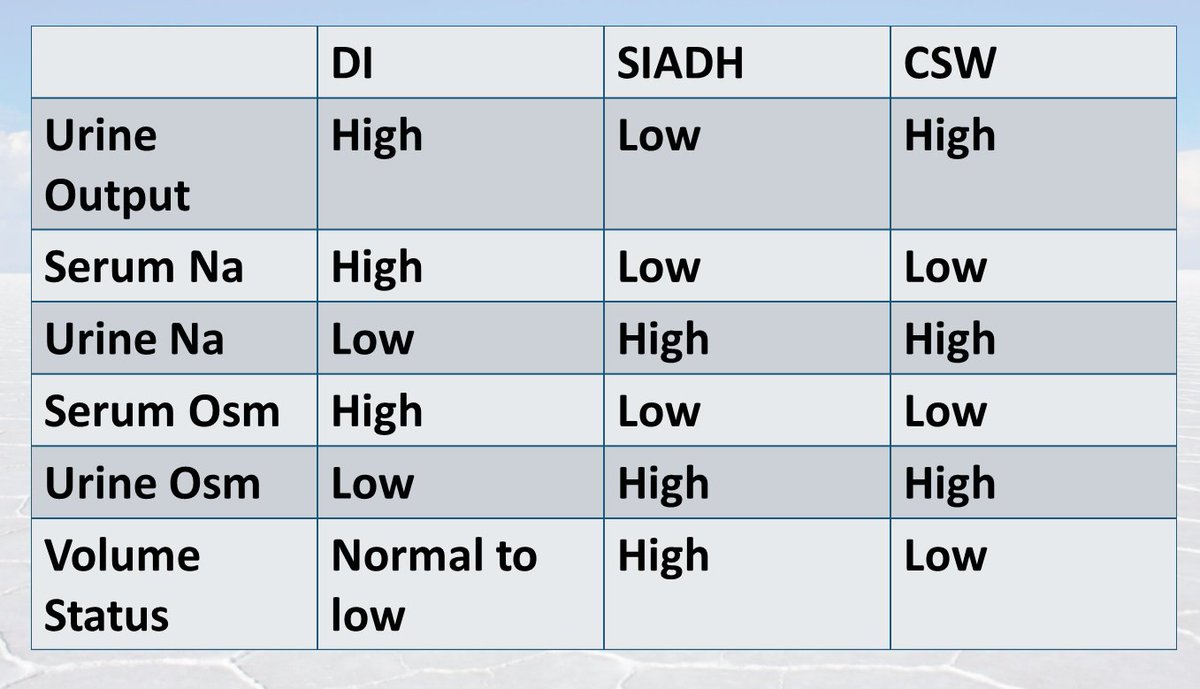
How you can tell the difference of diabetes insipidus vs siadh. diabetes insipidus: high urinary outputs, low levels of adh, high sodium levels, high serum osmolality, ongoing dehydration, and high levels of fluid loss. there may also be a genetic cause for this condition. siadh: low urinary outputs, high levels of adh, low sodium levels, low serum osmolality, being over-hydrated, and. Treatment of cerebral salt wasting is through frequent hydration to prevent dehydration plus medications. summary: 1. siadh is caused by infections and cancers while cerebral salt wasting is caused by brain trauma, injury, hematoma, and tumors all occurring in the brain. 2. siadh has a greater sodium urine concentration than cerebral salt wasting. Siadh vs cerebral salt wasting syndrome (csws) csws is usually associated with hypovolemia whereas patients with siadh are euvolemic. in addition, patients with siadh exhibit elevated adh levels and rarely develop urine sodium levels > 100 meq/l. patients with csws usually have normal adh levels and often develop urine sodium levels > 100 meq/l. Combined central diabetes insipidus and cerebral salt wasting syndrome is a rare clinical finding. however, when this happens, mortality is high due to delayed diagnosis and/or inadequate treatment. a 42-year-old white man was diabetes insipidus vs cerebral salt wasting referred to neurosurgery.
Central neurogenic diabetes insipidus (cndi), syndrome of inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone (siadh), and cerebral salt-wasting syndrome (csws) all affect both sodium and water balance; however, diabetes insipidus vs cerebral salt wasting they have differences in pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Cerebralsaltwasting; diabetesinsipidus; hyponatraemia is a common finding in patients with acute cerebral insults, especially after neurosurgical procedures for hypothalamic-pituitary tumours. it can be associated with the syndrome of inappropriate adh secretion (siadh), cerebral salt wasting (csw), treatment of transient/permanent diabetes.
Diabetes insipidus. in diabetes insipidus, or di, the body releases too less anti-diuretic hormone (adh). it is a disorder of water and salt metabolism marked by extreme thirst and heavy urination. diabetes insipidus di takes place when the body is unable to regulate the fluids. Diabetesinsipidus di is associated with tbi, sah, intracerebral haemorrhage, and pituitary surgery. the incidence of di can be as high as 35% after tbi when it is associated with more severe injury and increased mortality. 9 development of di in non-pituitary surgery is often associated with severe, pre-terminal, cerebral oedema.
Comments
Post a Comment