Diabetes Insipidus Jcem
Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. since the kidneys don't properly respond to adh in this form of diabetes insipidus, desmopressin won't help. instead, your doctor may prescribe a low-salt diet to help reduce the amount of urine your kidneys make. you'll also need to drink enough water to avoid dehydration. Diabetesinsipidus (di) is an uncommon condition with either relative or absolute lack of anti-diuretic hormone (adh) leading to inability to concentrate the urine and subsequent polyuria/polydypsia and potentially fluid and electrolyte imbalance. this can be seen in a variety of conditions in the paediatric population, most commonly in. Central di is associated with other endocrine autoimmune disorders. in one study, 26% of patients with central di had an associated autoimmune disorder most frequently hashimoto thyroiditis (16. 7%) and diabetes mellitus type 1 (5. 3%). pivonello r, de bellis a, faggiano a, et al. central diabetes insipidus and autoimmunity: relationship between the occurrence of antibodies to arginine.
5. maghnie m, cosi g, genovese e, et al. central diabetes insipidus in children and young adults. n engl j med. 2000; 343(14): pp. 998–1007. doi: 10. 1056/nejm200010053431403. 6. mao jf, zhang jl, nie m, lu sh, wu xy. diabetes insipidus as the first symptom caused by lung cancer metastasis to the pituitary glands: clinical presentations. Remember combination of eating well and sufficient amount of exercise is the diabetes insipidus jcem loss ketones urine weight best gestational diabetes treatment. diabetes insipidus jcem loss ketones urine weight you can select your glucose meter using the following criteria: amount of blood needed for the test. this digital infusion pump. Diabetes insipidus is a different disease than diabetes mellitus. despite the similar names, the only things these two have in common is that they make you thirsty and make you pee a lot. if you.
No additional pathologically proven cases of necrotizing hypophysitis have been reported thus far. a third diabetes insipidus jcem case appeared in the japanese literature and described a 14-yr-old boy with a prolonged history of diabetes insipidus, but the diagnosis was established without pituitary biopsy, so it is less certain. 1. Pivonello r, de bellis a, faggiano a, et al. central diabetes insipidus and autoimmunity: relationship between the occurrence of antibodies to arginine vasopressin-secreting cells and clinical, immunological, and radiological features in a large cohort of patients with central diabetes insipidus of known and unknown etiology.
Diabetesinsipidus The Journal Of Clinical Endocrinology
Diabetesinsipidus is a disorder of water homeostasis characterized by the excretion of abnormally large volumes of hypotonic urine. the once the type of di is determined, the clinical review and investigations can be directed to identify the underlying cause.

In a consanguineous palestinian family with neurohypophyseal diabetes insipidus, willcutts et al. (1999) identified a 301c-t mutation in exon 1 of the avp gene (192340. 0016), replacing proline-7 of mature avp with leucine (leu-avp). all 3 affected children were homozygous for the mutation, and the parents were heterozygous, suggesting autosomal recessive inheritance. Central diabetes insipidus. central di occurs when the secretion of adh (also called vasopressin) by the posterior pituitary is insufficient to meet urine concentration requirements. the prevalence of medically treated di is about 100 per 1 million inhabitants. Diabetesinsipidus is also common and may occur in up to half of patients [16, 19, 27, 42]. immunotherapy-associated hypophysitis often presents with headache and anterior hypopituitarism. the degree of pituitary enlargement is typically mild, and compression of the optic apparatus is very rare. Diabetes insipidus (di) is a metabolic disorder characterized by an absolute or relative inability to concentrate urine, resulting in the production of large quantities of dilute urine.
3 diabetes insipidus jcem diagnosis of central diabetes insipidus 3. 1 history and clinical examination. history and clinical examination occasionally yield useful diagnostic clues. a 3. 2 indirect tests. the most commonly used test for di is the two‐step water deprivation test. the first step is an 3. 3 direct tests. We are dedicated to providing the field of endocrinology with timely, evidence-based recommendations for clinical care and practice. we continually create new guidelines and update existing guidelines to reflect evolving clinical science and meet the needs of practicing physicians. Postop diabetes insipidus is a common, often transient complication of sellar and suprasellar neurosurgical procedures. this case study features a 28-year-old woman with new-onset vertigo and diplopia. Diabetesinsipidus is a condition where the body loses too much fluid through urination, causing a significant risk of dangerous dehydration as well as a range of other illnesses and conditions.
2016 Endocrine Society Guidelines Central Di Gerti
Diabetesinsipidus symptoms, diagnosis and treatment.
Diabetes insipidus (di) is a syndrome characterized by the excretion of an abnormally large volume of dilute urine (polyuria) and a commensurate increase in fluid intake (polydipsia). it is differentiated into 4 types based on etiology and therapeutic requirements ( 1, 2 ). Diabetesinsipidus occurs in the acute phase of tbi in 20% of cases, 2, 3 and in 15% of patients with sah. 4 di is almost always transient, and in both conditions, persistent di is associated with worse prognosis; persistent di is a common manifestation of increasing intracranial pressure and may presage the onset of coning. 3 careful follow‐up shows that di persists in only 7% of tbi. Diabetes insipidus (die-uh-bee-teze in-sip-uh-dus) is an uncommon disorder that causes an imbalance of fluids in the body. this imbalance makes you very thirsty even if you've had something to drink. it also leads you to produce large amounts of urine. while the terms "diabetes insipidus" and "diabetes mellitus" sound similar, they're not related.

Diabetes Insipidus Symptoms Diagnosis And Treatment Bmj
Diabetes insipidus is a rare disorder that occurs when a person's kidneys pass an abnormally large volume of urine diabetes insipidus jcem that is insipid—dilute and odorless. in most people, the kidneys pass about 1 to 2 quarts of urine a day. in people with diabetes insipidus, the kidneys can pass 3 to 20 quarts of urine a day. Diabetesinsipidus (di) is a metabolic disorder characterized by an absolute or relative inability to concentrate urine, resulting in the production of large quantities of dilute urine. it may result from an absolute or relative deficiency of arginine vasopressin (avp), also known as antidiuretic hormone (adh), which is produced by the. Diabetes insipidus background. diabetes insipidus (di) is an uncommon condition with either relative or absolute lack of anti-diuretic assessment. baseline investigations should include urea and electrolytes, full ward test of urine and paired serum and management. after assessment of level of.
Diabetes insipidus as a complication after pituitary surgery.
Both transient diabetes insipidus and the first phase of the triphasic pattern are thought to be caused by temporary dysfunction of avp-producing neurons, secondary to trauma to the connections. Although the articles here chiefly concern diabetes mellitus, a pilot study in jcem focuses on diabetes insipidus (whose main sign is excessive urination; the root of “diabetes” is the greek for “siphon”). aulinas et al. find suggestive evidence that patients who also have pituitary deficiencies suffer depression and anxiety as a result.
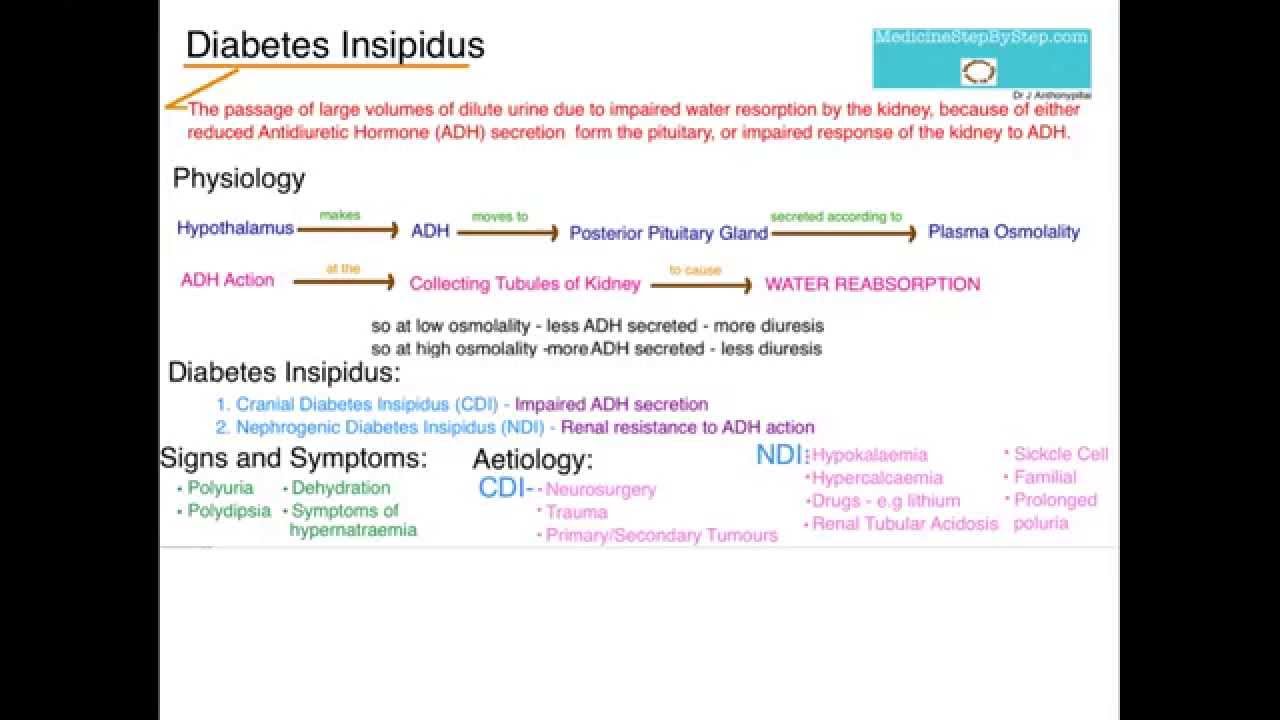
Diabetesinsipidus (di) is a hereditary or acquired condition which disrupts normal life of persons with the condition; disruption is due to increased thirst and passing of large volumes of urine, even at night. a systematic search of literature for di was carried out using the pubmed database for the purpose of this review. Diabetes insipidus (di) is a condition in which the kidneys are unable to concentrate urine. central di, the most common form of diabetes insipidus, is caused by insufficient levels of circulating antidiuretic hormone (adh); nephrogenic di, however, is characterized by defective renal adh receptors in the kidneys. Diabetesinsipidus (di) is a syndrome characterized by the excretion of an abnormally large volume of dilute urine (polyuria) and a commensurate increase in fluid intake (polydipsia). it is differentiated into 4 types based on etiology and therapeutic requirements (1, 2).
Diabetes insipidus, also called di, is a rare condition that leads to frequent urination (passing a lot of clear urine) and excessive thirst. the condition may be caused by problems with your pituitary gland and/or your kidneys. Diabetesinsipidus, also called di, is a rare condition that leads to frequent urination (passing a lot of clear urine) and excessive thirst. the condition may be caused by problems with your pituitary gland and/or your kidneys.


Comments
Post a Comment